Milliseconds matter. If you are a stockbroker in New York, your internet’s millisecond advantage over a stockbroker in San Francisco may translate into millions of dollars.
However, it’s not just a matter of money. For pretty much all companies on the internet, the first objective is to get traffic to your website and keep visitors engaged. If you have an international company in California and target users in Japan, a server located on the West Coast will not serve up your solution as quickly as a server in Osaka would – and your potential visitor may leave before the page has even loaded.
Not to worry: CDNs to the rescue!
What is a CDN?
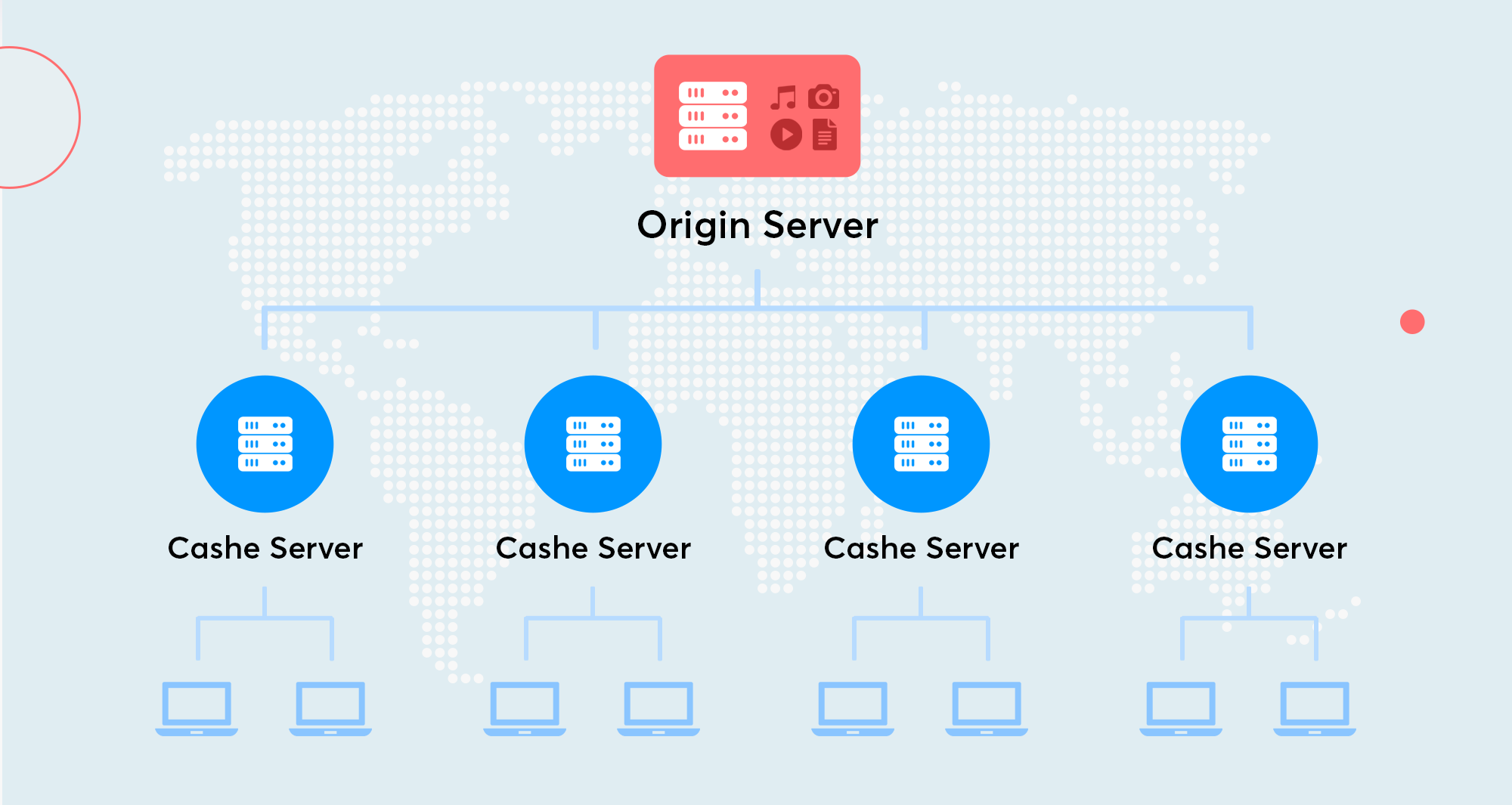
A Content Delivery Network is simply a set of servers placed in various locations around the globe.
The purpose of these servers is to speed up the delivery of web pages to end users in these locations. In this way, a user located in China is served a web page from a CDN in China rather than one in Spain, gaining important milliseconds or seconds in load time.
How does a CDN work?
A CDN consists of “mirror” servers which store cached content from the original server and hold it in Points of Presence (PoPs) around the world. When a request is made, the CDN identifies the nearest server and activates it to deliver the content to the end user.
Think of the Amazon warehouse system. Amazon did not build a city-sized warehouse in Seattle that serves the entire world. Instead, it built a network of warehouses around the world and simply computes the warehouse nearest to your address that holds the item you’re ordering.
Similarly, a Content Distribution Network simply computes the shortest distance the content needs to travel to reach the end user.
Benefits of using a Content Delivery Network
Now that the “what” is clearer, let’s tackle the “why”: why do websites big and small use CDNs? There are several already obvious benefits, as well as a couple of quite surprising ones.
Reduced latency
The biggest and most obvious one is generally called “reduced latency”. The requested content is delivered faster because it is delivered from a closer location.
With this reduced latency comes the added benefit of your visitors’ improved user experience. Your pages, for instance, will be more stable and able to display larger images or video files faster, with less distortion or buffering.
Website stability
Server crashes and network overload are always potential issues when you place all your eggs in one basket (that is, all your delivery capacity in one location). With a CDN, your website’s content availability will be higher thanks to less pressure on the “origin” server and network. Your up time will be higher to 100% and your sleep much better.
Improved security
Most CDNs also offer a high level of protection against DDoS attacks. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are malicious attacks against a website, conducted by flooding its resources (bandwidth, server capacity) with requests from multiple sources. As these requests are too numerous to handle, the server crashes and the website becomes unavailable.
Content Delivery Networks inherently make it highly improbable that such attacks are successful; CDNs distribute mirrored content across the network and by systems of DDoS detection and mitigation.
On top of that, most CDNs also offer SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) support, another big plus.
Surprise factor 1: Lower costs
Because they offer cached content and various optimizations that minimize the amount of bandwidth, CDNs are also a money saver. Bandwidth consumption can be a serious cost if you run a resource-intensive website, so lowering the amount of data that eats up point-of-origin bandwidth is a good deal. However, that advantage needs to be balanced, of course, against the cost of running the CDN. Read on to see how you can choose the right CDN for your needs.
Surprise factor 2: Improved page ranking
The surprising value-added effect here is that there is a clear opportunity for improvements in page ranking.
Your Core Web Vitals score (Google’s way of measuring on-page latency and user experience) will likely be higher: less content shifting and more visual stability, less packet loss, and generally a better page performance. With these improvements, visitors will engage more and search engines will rank your website higher.
Tips for choosing a CDN
- Number and location of nodes. Depending on how big (and international) your business is, the number of nodes can be a dealbreaker. Don’t choose the biggest number just because you can; choose a provider that has enough nodes in the right places to hit your target audience.
- Speed. Quite an obvious one: To provide the best user experience, choose a fast CDN. However, if in doubt, always look at speed second and at location first.
- Reliability. Sometimes, costs are lower at the expense of reliable performance. Make sure you don’t get a cheap deal instead of a good deal. Check end user testimonials and, as much as possible, look into the history of the provider.
- Customer service. Not so obvious, but essential. You want a CDN provider that will pick up your call and support you in an emergency.
- Cost. Another obvious one: you pay for a lemon, you get a lemon. The problem is how to balance cost and all the other requirements. Our advice is to first determine your needs and only then look at the costs.
Conclusion
To choose the right CDN for you, start by asking the right questions.
What is the size of your audience today? Where are your visitors located and how are they distributed across these locations? How secure is your current website? Do you do e-commerce or plan to? How much resource-intensive content do you have?
Once you understand your needs, you will be able to make the best choice. Good luck & may the content delivery work ever in your favor!